Used Car Batteries Toronto
A car battery is a device that stores energy and can be charged. It is used to power the electric parts of a car. It is an important part of a car because it gives the engine the power it needs to start and runs the lights, radio, and other electrical parts.
What are car batteries made of?
The car battery is made up of lead-acid cells that store chemical energy. When electricity is needed, chemical energy is turned into electrical energy. Inside the battery, the lead plates are separated by a porous material that holds a solution of sulfuric acid and water called the electrolyte.
The primary role of the battery is to store and supply electrical energy to the starter motor, which is in charge of starting the engine when the key is turned. The battery also powers the vehicle’s electrical components, such as the lights, radio, and power windows.
What happens to used car batteries?
Most of the time, used car batteries are recycled so that the lead, plastic, and other materials they contain can be reused. In the recycling process, the battery is broken down into its individual parts. These parts are then separated and used to make new batteries and other products. In many cases, the lead is melted down and made into new battery plates, while the plastic is melted down and made into new battery cases.
Recycling old car batteries save natural resources, cuts down on trash in landfills, and reduces the damage that making batteries does to the environment. Used batteries can also be a source of income for people who collect and recycle them because they can be used to get valuable materials.
What are the types of car batteries?
Car batteries are commonly classified into four types:
- Traditional lead-acid: When compared to the other types, the lead-acid battery has the lowest maintenance costs. This particular battery, in contrast to others, is sealed up, which means that it cannot be maintained and must instead be switched out for a new one when it approaches the end of its product life cycle.
- Starting, Lighting, and Ignition (SLI): These batteries are lead-acid batteries that are made to provide the high current needed to start an internal combustion engine. Compared to deep-cycle batteries, they tend to be smaller and have less power, but they can deliver high currents for short periods of time. Most cars, trucks, and other vehicles with internal combustion engines use SLI batteries.
- Lithium-ion: As the name suggests, lithium-ion batteries store and release energy in the form of lithium ions. In comparison to other rechargeable battery types, they have a high energy density, low self-discharge, and a long lifespan. Numerous mobile electronics, electric cars, and alternative power sources rely on lithium-ion batteries.
- Absorbed glass mat (AGM): Absorbent Glass Mat (AGM) batteries are a type of lead-acid battery that uses a fiberglass mat to absorb and hold the electrolyte. This design helps prevent spills, extends the life of the battery, and makes the flow of electricity more efficient. AGM batteries absorb sulfuric acid and provide a greater degree of performance and longevity.
What are the best brands of car batteries?
With so many choices on the market, it can be hard to figure out which brand of a car battery is best for you. Here are some of the best car battery brands featured in trusted organizations such as Consumer Reports and Motor1.com and what makes them stand out.
- ACDelco – ACDelco is a well-known vehicle battery company with a reputation for quality and dependability. Many drivers use ACDelco batteries because they are intended to provide constant power and performance. Furthermore, ACDelco offers great customer service and a robust guarantee, giving drivers peace of mind when it comes to their batteries.
- Bosch is one of the most popular automobile battery brands. The brand provides a wide range of car batteries that are designed to fulfill the particular needs of various types of vehicles. Their dependability and long lifespan make them a popular choice for many drivers. Furthermore, Bosch offers great customer service and a strong warranty, giving drivers peace of mind when it comes to their batteries.
- Car batteries from the Optima brand are highly acclaimed due to their cutting-edge technology and reliable performance. Optima batteries are a popular option for drivers who seek a battery that can withstand harsh driving conditions and demanding electrical systems because of their design to give high levels of power and durability. They have a variety of solutions for various automobiles, making it simple to select the most appropriate battery.
How are used car batteries recycled?
Car batteries are essential for powering vehicles, but when they reach the end of their useful life, they must be properly disposed of. Recycling used car batteries is an important method that helps to conserve natural resources and lessen the negative environmental impact of wastage. The standard procedures involved in the recycling of used automobile batteries are as follows:
- Used car batteries must first be gathered and transported to a recycling facility. Battery recycling centers typically handle this, as they gather batteries from various locations such as garages, car lots, and junkyards. The batteries are subsequently taken to a facility where they will be recycled.
- Upon arrival at the recycling center, the batteries are separated and treated to remove all insulation and plastics. They are then separated for their own recycling process.
- Preparing the plastic parts of the battery for recycling begins with cleaning and drying them. Once that’s finished, the plastic is melted until it’s nearly liquid. Plastic pellets are made by forcing molten plastic through an extruder. The cases for new car batteries are made out of these pellets.
- Then, a process called “smelting” is used to get the lead and acid out of the batteries. During this process, the lead is melted and poured into molds to make sheets and blocks of lead. Lead is first melted in the furnace, and then the molten metal is poured into ingot molds after it has been liquefied. After a few minutes, the impurities that were discovered in the lead will rise to the surface, at which point they can be effortlessly extracted. After the impurities have been extracted, the ingots are then left to gradually become more solid by cooling down. After the ingots have cooled and solidified, they are removed from the molds. They are then shipped to battery factories where they are remelted and recycled into new battery cells. Sodium sulfate, a common ingredient in detergents and other household products, is made by neutralizing the acid and processing it.
How do I boost a car battery?
Boosting a car battery is using a jump starter to get a vehicle started with a dead or weak battery. The procedure for charging an automobile battery is as follows:
Get The Tools Ready
Jumper cables, a car with a good battery, and safety goggles are required tools.
Position The Cars
Place the cars such that the one with the dead battery is close to the one with a working battery, but make sure they don’t touch. Both cars should be turned off.
Connect The Positive Cables
Connect the positive cables by connecting one red cable clamp to the positive terminal of the good battery and the other to the positive terminal of the dead battery.
Connect The Negative Cables
Attach one black cable clamp to the good battery’s negative terminal. Then, secure the other black cable clamp to a metal element of the car that is not near the dead battery, such as a bolt on the engine block.
Double-Check
Stop and check again to make sure that all connections are safe.
Start The Engine
Ask your helper to rev the engine of the donor car a little bit, but not too much. With a good battery, start the vehicle and let it run for a few minutes to allow the battery to charge. Then, with the dead battery, try starting the vehicle. If it doesn’t start the first time, wait a few minutes and try again.
Disconnect The Cables
Once the car with the dead battery has started, allow both vehicles to idle for a few moments and gently disconnect the jumper wires in the reverse sequence in which they were connected. Remember not to let any of the four cable ends come into contact with each other or either vehicle.
Keep The Car Running
Do not turn off the car with a discharged battery until it has been sufficiently recharged by the alternator. Typically, 25 kilometers or half an hour should be enough to recharge it to restart. It is important to note that if the engine is only idling, it may not recharge, especially if the lights, heating fan, or other accessories are turned on.
When attempting to give a car battery a boost, it is essential to take all necessary safety precautions, as incorrectly connecting the jumper wires can result in damage to the batteries as well as the automobiles.
How long does a car battery last?
A car battery, like all batteries, has a limited lifespan and will eventually need to be replaced. The lifespan of an automobile battery is determined by several factors, including usage, environment, and battery quality.
An automobile battery should last between 3 and 5 years on average. However, depending on the circumstances, this lifespan can be shortened or extended. For instance, if a car is driven frequently and for long distances, the battery will last longer. In contrast, if a vehicle is rarely driven or is left unused for long periods of time, the battery life will be reduced.
Aside from usage, the environment influences the longevity of a car battery. Extreme temperatures, such as hot summer days or freezing winter nights, might harm the battery. In severe temperatures, the battery may discharge faster, lowering its overall lifespan.
Another aspect that influences the lifespan of a car battery is battery quality. A high-quality battery built of premium materials will often last longer than a lower-quality, cheaper battery. To ensure maximum performance and lifespan, choose a battery that is built for your specific vehicle and satisfies the manufacturer’s standards.
WE SELL BULK CAR BATTERIES
IF YOU ARE A BUYER,
HOW TO CHANGE/REPLACE A CAR BATTERY
Changing a car battery is a simple task that requires only a few basic tools. Here’s how to replace a car battery step by step:
Purchase a New Battery
Select a battery that is specifically built for your vehicle’s make and model and satisfies the manufacturer’s criteria.
Gather Your Tools
A socket set, pliers, a wrench, and a battery brush are all required.
Locate The Battery
The battery is often found in the engine compartment and is easily identified by its size and shape.
Disconnect The Negative Cable
Remove the negative cable from the battery’s negative terminal with a wrench. This is commonly denoted by a “-” symbol or the color black.
Disconnect The Positive Cable
Remove the positive cable from the battery’s positive terminal with a wrench. This is commonly indicated by a “+” symbol or the color red.
Remove The Old Battery
By unscrewing the battery hold-down bracket and lifting the old battery out of the car.
Clean The Battery Tray
To clean the battery tray and remove any corrosion, use a battery brush and baking soda combined with water.
Install The New Battery
Insert the new battery into the tray and secure it with the battery hold-down bracket.
Connect The Positive Cable
Connect the positive cable to the new battery’s positive terminal. Check that the cable is securely attached.
Connect The Negative Cable
Connect the negative cable to the new battery’s negative terminal.
Check The Battery
Start the car and ensure that the battery is generating enough power to start the engine.
How do I charge a car battery?
You can charge a car battery in a number of ways, such as by using a battery charger or jump-starting the car. Here’s how to charge a car battery step by step:
- Find out what kind of battery it is: Check the type of battery because different types of batteries need to be charged in different ways. A lithium-ion battery needs to be charged in a different way than a lead-acid battery, which is the most common type of car battery.
- Buy a battery charger: If the battery needs to be charged, buy a battery charger made for the type of battery you have in your car.
- Connect the charger: Connect the positive and negative clamps of the battery charger to the positive and negative terminals of the car battery.
- Set the charging rate: Set the battery charger’s charging rate to what the manufacturer recommends. Most of the time, a slow charge is best to keep the battery from getting too full.
- Charge the battery: Turn on the battery charger and let it charge the battery until it reaches the level of charge you want, which is usually shown on the charger by a light or a gauge. How long it takes to charge will depend on the size of the battery and how fast it charges.
- Disconnect the charger: Turn off the charger and take the clamps off the battery terminals when the battery is fully charged.
If you can’t charge the battery with a charger, you might be able to jump-start the car. Here are the steps you need to take to jump-start a car battery:
- Get a jump-starting kit: You can buy or borrow a jump-starting kit, which usually includes a set of cables and a working car.
- Find the batteries: On both cars, open the hoods and look for the batteries.
- Connect the positive clamps: Plug one positive clamp into the positive terminal of the dead battery and the other positive clamp into the positive terminal of the working battery.
- Connect the negative clamps: Connect one negative clamp to the negative terminal of the working battery and the other negative clamp to a metal surface on the engine block of the dead car.
- Start the vehicle: Start the vehicle that is being used and let it run for a few minutes.
- Attempt to start the dead car: Try to start the dead car. If it starts, let it run for a few minutes so the battery can get charged.
- Disconnect the cables: Once the dead car is running, turn off both cars and remove the jump-starting cables in the opposite order of how they were connected.
How do I disconnect a car battery?
A car battery can be disconnected quickly and easily by following a few easy procedures:
- Locate the battery: The battery is often found in the engine compartment and is easily identified by its size and shape.
- Open the hood: To reach the battery, open the hood of the car.
- Find the battery terminals: The battery has two terminals, one positive (+) and one negative (-). (-).
- Disconnect the negative cable: Remove the negative cable from the negative terminal with a wrench. The negative wire is typically black and marked with a “-” sign.
- Disconnect the positive cable: Remove the positive cable from the positive terminal with a wrench. The positive cable is normally red and is denoted by a “+” symbol.
- Close the hood: Keep the cords away from the battery terminals to prevent inadvertent contact and potential sparking and close the hood.
It is crucial to note that disconnecting the battery will result in the loss of the electrical power stored in your car’s battery, and certain systems, such as the radio, may need to be reset after reconnecting the battery.
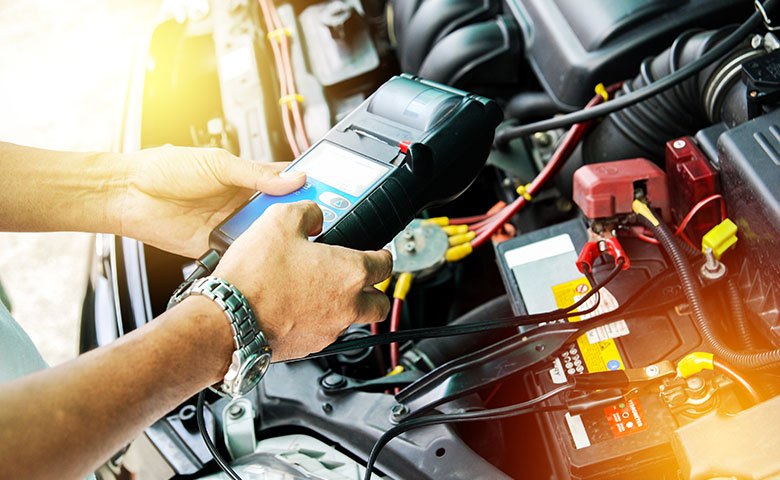
How do I test a car battery?
Testing a car battery is a crucial step in maintaining your vehicle’s electrical system. A car battery can be tested using a variety of tools, including a multimeter, a hydrometer, or a battery load tester. Here’s how to test a car battery using a multimeter:
- Gather your tools: You’ll need a digital multimeter, which is a cheap gadget that you can get from an automotive supply store.
- Locate the battery: The battery is often found in the engine compartment and is easily identified by its size and shape.
- Set the multimeter: Set the multimeter to “DC volts” mode.
- Connect the multimeter: Attach the red lead to the positive terminal of the battery and the black lead to the negative terminal.
- Make a note of the reading: Take note of the reading from the multimeter. A completely charged battery should have a voltage reading between 12.6 and 12.8 volts.
- Start the engine and take another reading: Start the engine and take another reading. When the voltage rises to at least 13.7 volts, the alternator is charging the battery.
- Check the electrical parts: Check for a load by turning on the headlights, heating fan, and any other electrical devices in the car while the engine is still running. The voltage must not fall below 11 volts.
- Disconnect the multimeter: When the tests are finished, remove the multimeter from the battery and turn off the engine.
How much is a car battery?
The price of a car battery in Ontario can vary depending on a variety of different factors, such as the type, brand, and size of the battery. A standard lead-acid car battery costs around $100 on average, while premium and high-performance batteries can cost more than $300.
Keep in mind that pricing might vary from store to store, so it’s always a good idea to do some comparison shopping before making a final purchase. Be sure to add the cost of installation, which is offered by some auto parts retailers and dealerships for a fee, to its overall cost. We also offer batteries at Towing and Scrap Removal, which you can purchase in bulk. Feel free to contact us here for more details.
FAQ
How many volts are in a car battery?
Most car batteries are 12-volt batteries. The standard car battery is made to give the car’s electrical system a certain voltage, which is usually 12 volts. This voltage is what gives the car’s electrical parts, like the headlights, radio, and power windows, the power they need to start the engine and work.
How do I remove a car battery?
To take out a car battery, you must first find it in the engine bay and open the car’s hood. Then, find the terminals on the battery and use a wrench to remove the negative cable from the negative terminal. Next, do the same thing with the positive cable. Keep the cables away from the battery terminals so they don’t get tangled up. After these steps, you can safely take the battery out of the car.
Is it safe to replace my car battery myself?
Yes, it is safe to change your own car battery as long as you take the right precautions and follow the instructions from the manufacturer. But you should take some safety precautions to avoid getting an electric shock or damaging the car.
What is a battery booster?
A battery booster is a device that can be used to temporarily jump-start a car’s battery when it has run out of power, usually by connecting it to a separate, charged battery. Most of the time, cables are used to connect the booster’s battery to the vehicle’s battery. This gives the engine a burst of energy to start. Jump starters and jump packs are two other names for battery boosters.
How much is a battery booster?
The cost of a battery booster might change significantly based on its storage capacity, the functions it includes, and the manufacturer. The price of a basic model can range anywhere from $30 to $100, while the price of a more sophisticated one can be several hundred dollars.
What should I consider when buying a car battery?
There are several factors to consider when buying a car battery, such as the size and type, Cold Cranking Amps (CCA) for starting power in cold weather, reserve capacity for supplying power to the electrical system, warranty coverage, brand reputation, and price in relation to the battery’s specifications and any extra services offered, including installation and guarantees. Make sure the battery you choose meets the requirements in the owner’s manual for your car for reliable performance.